Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Controller
820Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Controller
DetailsSite Search
The term “servo motor” originates from the Greek word meaning “slave,” signifying its ability to faithfully execute control signal commands. In the modern field of industrial automation, servo motors play a crucial role, allowing precise control of position, speed, acceleration, and torque. Key features of servo motors include rapid response speed, high precision, swift acceleration and deceleration, with speed performance unaffected by load. Additionally, they offer a wide speed range, good high-speed performance, smooth low-speed operation, and strong overload capacity, being able to withstand loads up to three times the rated torque. This makes them especially suitable for applications where instantaneous load fluctuations and quick start-ups are required.
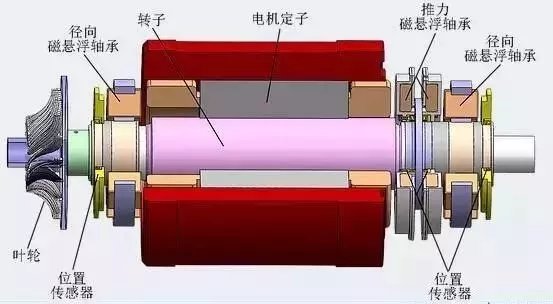
Internal Structure Explanation:
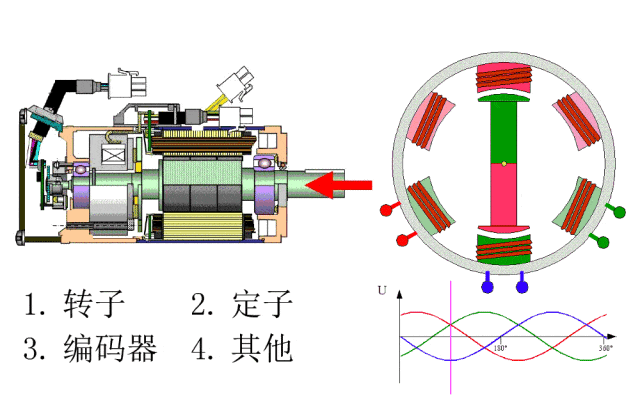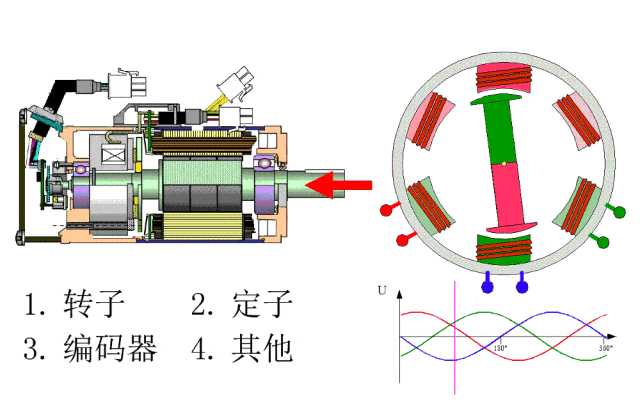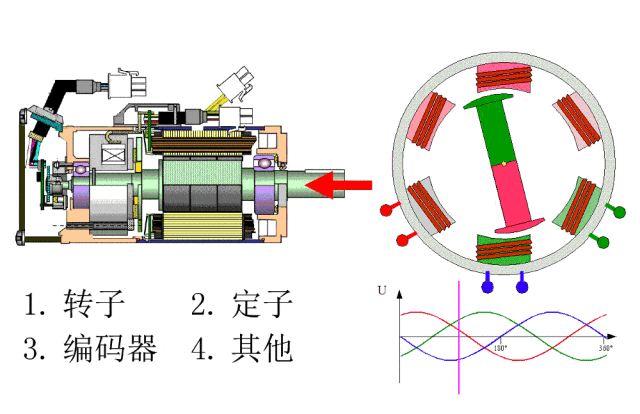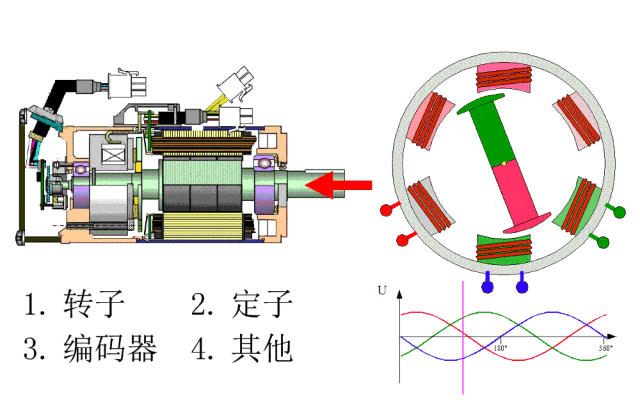
The internal structure of a servo motor is intricate, consisting mainly of two parts: the stator and the rotor. The stator includes two key windings: the excitation winding and the control winding. The rotor is made of either a permanent magnet or an induction coil which allows it to rotate under the influence of the rotating magnetic field generated by the excitation winding. Importantly, servo motors also have built-in encoders. This design enables the driver to receive real-time feedback signals from the encoder and compare these with the target value, thereby precisely adjusting the rotor’s rotational angle. This mechanism ensures the high accuracy of servo motor control, with the encoder’s precision largely determining the motor’s overall control accuracy.
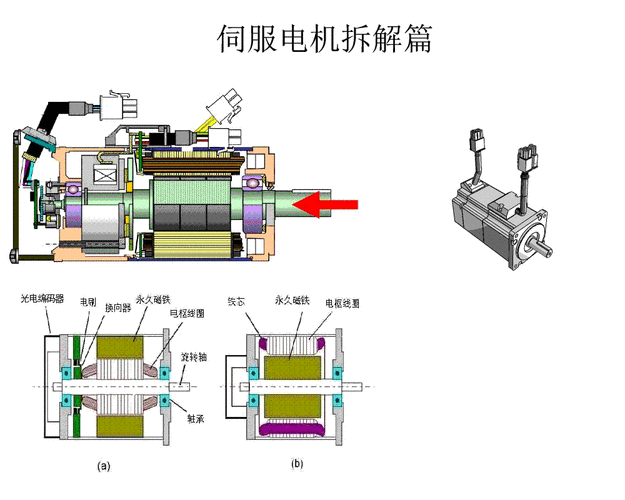
Working Principle:
The servo motor system is a complex whole, consisting of the servo driver, motor, and other related components. Within this system, the servo motor provides power, while the servo controller is responsible for adjusting output speed and position, translating these adjustments into electrical signals that are sent to the actuators. Specifically, a servo motor typically consists of an induction motor and a rotor, referred to as a flywheel. As the rotor spins, it generates a magnetic field that drives another small mechanical component within the motor. The coil on the rotor is closely linked to a suction cup, which is responsible for winding the wire around the top of the rotor, giving the motor its unique form. Meanwhile, the presence of gear mechanisms ensures the rotor’s smooth rotation and effectively reduces noise.
Classification and Features:
Servo motors can be categorized into DC servo motors and AC servo motors, depending on the type of current. DC servo motors are further divided into brushed and brushless motors. Brushed motors are low-cost, have simple structures, large starting torque, a wide speed range, and are easy to control but require regular maintenance. Brushless motors are compact, lightweight, offer large output power, fast response, high speed, and low inertia, and feature stable torque, smooth operation, and maintenance-free designs, making them suitable for various environments. AC servo motors are divided into asynchronous and synchronous types, known for good speed control characteristics, high efficiency, low noise, and the absence of brush wear, although they are more complex to control and require more wiring.
Servo motors, as a core component of industrial automation, are experiencing steady market growth alongside industrial automation upgrades. This growth is driven by two main demand factors:
Replacement Demand: In traditional fields such as machine tools, textile machinery, printing machinery, and packaging machinery, servo motors are gradually replacing stepper motors due to their advantages in precision, torque, and overload performance, with increasing penetration rates.

New Demand: The rapid development of emerging industries such as industrial robotics and electronic manufacturing equipment has significantly raised the demand for precision and performance, contributing substantial growth to the servo motor market.

According to authoritative data, the global servo motor market reached 36.7 billion yuan in 2020, and it is projected to grow to 53.9 billion yuan by 2026. In the Chinese market, the development of servo motors started later, but it has seen rapid growth in recent years. In 2020, the Chinese servo motor market was valued at 14.9 billion yuan, and it is expected to reach 22.5 billion yuan by 2026. However, the current competitive landscape of the servo motor industry is dominated by foreign brands, with the high-end market being almost entirely monopolized by them. Specifically, foreign brands hold a 65% share of the Chinese servo motor market, while domestic brands account for only 35%.
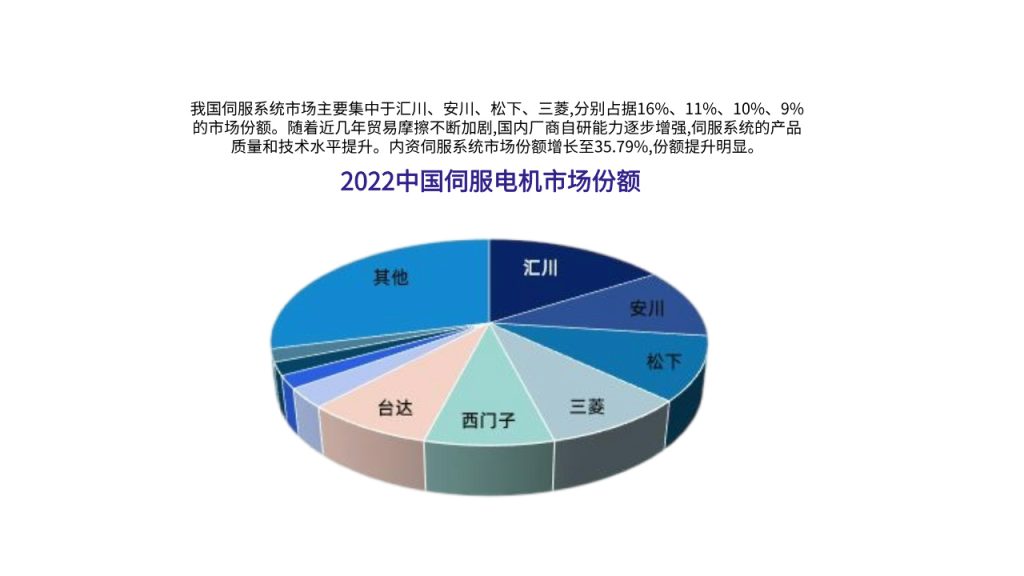
In terms of competition, European, Japanese, and domestic brands exhibit distinct characteristics. European brands such as Siemens and Lenze are known for high overload capacity, excellent dynamic response, and strong drive openness, though they are expensive and bulky. Japanese brands like Yaskawa and Mitsubishi dominate the mid-range market due to balanced performance and cost, compact size, light weight, reliability, and stability. Domestic brands such as Delta and Inovance have achieved large-scale production in the low to mid-range market but have yet to commercialize or mass-produce for the high-end market. Despite this, with continuous improvements in domestic servo technology and increased policy support, China is accelerating its efforts to substitute imports of servo systems.

In conclusion, as a core component of modern industrial automation, the market status of servo motors is increasingly prominent. In the future, with continuous industrial automation upgrades and the rapid development of emerging industries, the servo motor market will have broader development prospects. At the same time, domestic servo motor brands will face more opportunities and challenges, requiring continuous efforts in technological innovation, product quality, and market expansion to enhance their competitiveness and capture more market share.
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Controller
DetailsThis website uses cookies to improve your browsing experience. By continuing to use this site, you accept the use of our cookies.
Data collected from this website is processed and stored in the United States.
See Our Privacy Policy
Hello!Please login